- Supported by hardware.
- Include Short Integer, Integer, Long Integer, Unsigned Integer.
- Sign-magnitude notation vs. Twos complement (to store a negative number)
Sign-magnitude notation: the sign bit is set to indicate negative
and the remainder of the bit string represents
the absolute value of the number.
It does not lend itself to computer arithmetic.
Twos complement: taking the logical complement of the positive version of the number
and adding one. It is conveniert for addition and subtraction.
How do you add 7 and -3?
-310=complement of (00000011)2 + 1=(11111100+1)2=111111012
00000111
+ 11111101
100000100 Take away overflow and get 1002=410
Ones complement: taking the logical complement of its absolute value.
It has two representations of zeros.
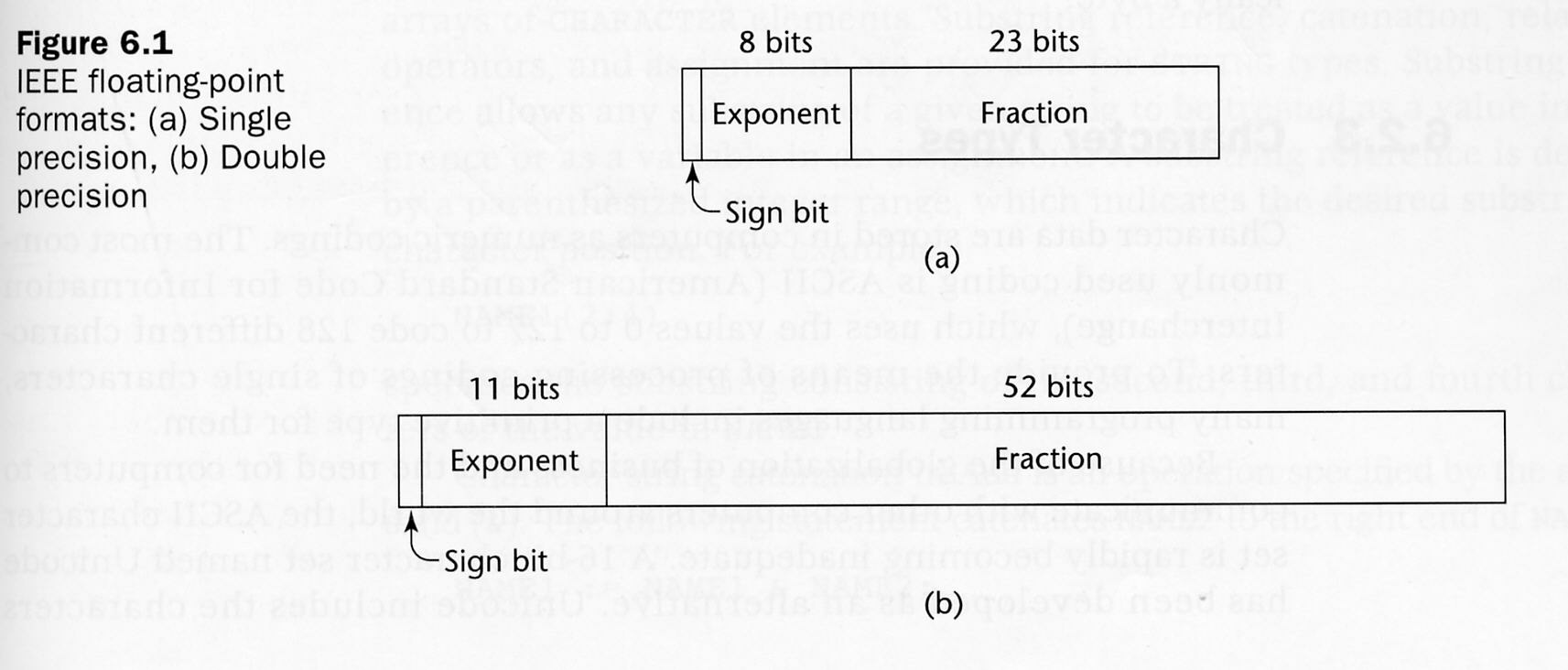
- Approximations of real values
- e.g. pi ->3.14 e 1275.33333……
- Scientific notation (factor & exponent)
- Float – 4 bytes
- Double – bigger fraction part, more precise.
- Floating Points Representation
See Figure 6.1
- Supported by COBOL
- Fixed numbers of decimal digits.
- Waste of memory but accurate in defined range.