Character String Types
Design Issues:
-
Should strings
be special type or primitive?
-
Should strings
have static or dynamic length?
Operations in Ada:
-
Substring reference:
-
Substring reference allows any substring of a given string to be treated
as a value in a
reference or a variable in an assignment.
-
e.g. NAME1(2:4)
-
the substring consisting of the 2nd,3rd, and 4th
character of the value in NAME1.
-
Catenation
-
e.g. NAME1 := NAME1 & NAME2;
-
If NAME1 = "PEACE", NAME2 = "FUL"
then NAME1 = "PEACEFUL".
-
Relational operations
-
Assignment
In general, both assignment and comparison operations on character
strings are complicated
by possibility of assigning and comparing operands of different lengths.
For example, what
happens when a longer string is assigned to a shorter string or vice
versa?
C, C++: use char
array to store strings and string terminated by NULL.
This is alternative to maintaining the length of string variables.
(header files: string.h or string (library functions:
strcpy, strcmp, strlen and operator overload)
)
FORTRAN, BASIC treat strings as a primitive type.
JAVA String class and StringBuffer
class
In Java, strings are supported as a primitive type by the String class,
whose values are constant strings,
and the StringBuffer class, whose values are changeable and are more like
arrays of single characters.
Subscripting is allowed on StringBuffer variables.
SNOBOL4, Perl pattern match
(see page 240)
Patten matching is provided by library function rather than an operation
in other languages.
String Length
static length
FORTRAN, COBOL, Pascal, Ada, Python, Java's String class
limited dynamic length C, C++ (Do not check range of index,
there is null at the end)
dynamic length
JavaScript, SNOBOL4, Perl (Use Linked List
or Adjacent Storage Cells to implement)
Descriptor (Compile Time Descriptor, Run-Time Descriptor) has three fields:
(See figures 6.2 and 6.3 on page 229)
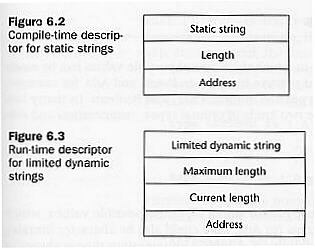
-
Name of the type: e.g. static string, limited dynamic string or
dynamic string.
-
Length: limited dynamic strings have two items: (maximum length,
current length)
-
Address of the first character
Dynamic length strings require more complex storage management. (allocation
and de-allocation take time.)
- strings can be stored in a linked list. A new location can be
anywhere in the heap.
- strings are stored as arrays of pointers to individual characters.
- strings are stored in adjacent storage cells. If grow too much,
move whole set to another location.
