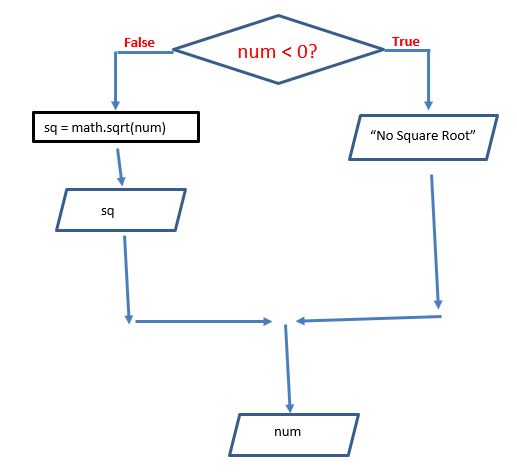
import math
num = int(input("Enter an integer: "))
if num < 0:
print("There is no square root of ", num,".", sep='')
else:
sq = math.sqrt(num)
print("The square root of ", num, " is ", sq, ".", sep='')
print("You entered ", num,".", sep='')
The condition is checked only one time.
When condition is true, do the block between if and else
and skip rest of part to go to the next statement.
When condition is false, skip the block before else
and do the block after else, then go to the next statement.