The Concepts of Binding and Binding Times
Binding -
any association, e.g. an attribute and an entity or an operation and a
symbol.
Binding Time - the time at which
a binding takes place.
Bindings can take place at
-
language design time
Set of possible types for a variable
Set of possible meanings for an operator symbol
-
language implementation time
A data type, such as INTEGER in FORTRAN, is
bound to a range of possible values.
-
compile time
A variable is bound to a particular data type.
-
link time
A call to a library subprogram is bound to
the subprogram code.
-
load time
A static variable may be bound to a
memory cell
when the program is loaded into memory.
-
run time
bind a nonstatic
local variable to a memory cell
Static Binding
- occurs before run time & remains unchanged as program runs.
A binding is
static
if it first occurs before run time
and remains unchanged throughout program execution.
Dynamic Bindings -
occurs during run time or can change during case of execution.
A binding is
dynamic
if it first occurs during execution
or can change during execution of the program

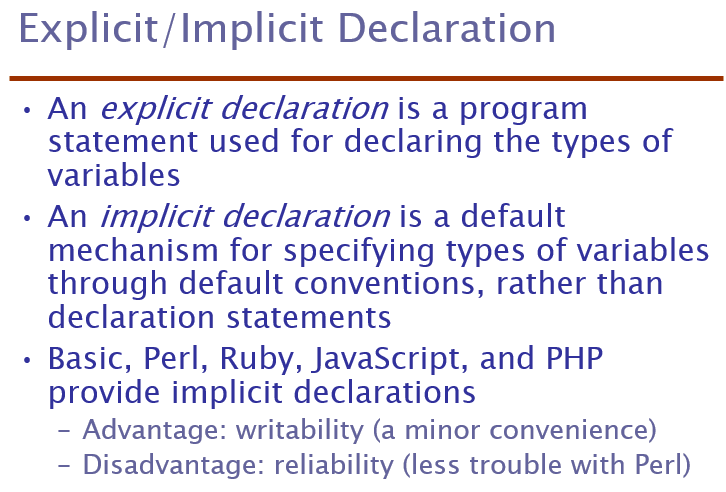


Declaration:
Specify type
Not cause allocation of storage
Definition:
Specify attribute
Cause storage allocation
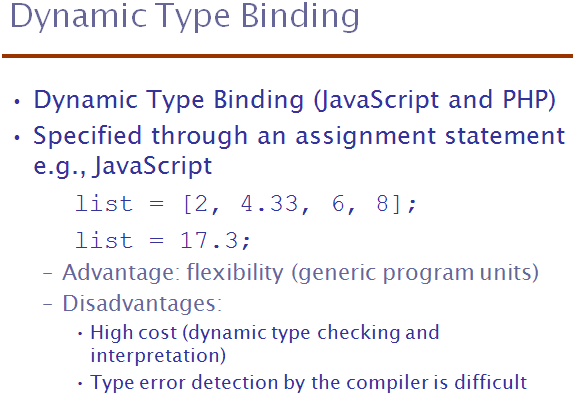
Dynamic Type Binding - Variable is bound to type when it is assigned
a value.
Advantage: Programming flexibility
Disadvantage: Hard to detect errors and cost more.
See page 190 for Type Inference ( Type can be inferred from the
type of constant in the expression)

Categories of Storage Bindings:






