and remain bound to those same memory cells until program execution terminates.
e.g. globally accessible variables (FORTRAN I, II and IV)Advantage: efficient (direct addressing), history-sensitive subprogram support
e.g. C, C++, and Java include the static specifier on local variable definition
e.g. Pascal does not provide static variables.
Disadvantage: lack of flexibility, no recursion supported
//extract a character from the string.
//static will remember last position.
char lexical()
{
static
int position = -1;
position = position + 1;
return text[position];
}
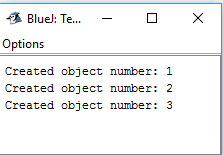
//Java Programming public class Stuff {
// Set count to zero initially.
static int count = 0;
public Stuff() {
// Every time the constructor runs, increment count.
count = count + 1;
// Display count.
System.out.println("Created object number: " + count);
}
}
|
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stuff stuff1 = new Stuff();
Stuff stuff2 = new Stuff();
Stuff stuff3 = new Stuff();
}
}
|